| |
|
|
|
Engine-driven
Chillers
|
| |
|
| |
| Electrical
chillers are the single largest electrical load in many
commercial facilities. Engine-driven
Chillers can be an attractive alternatives to these costly electrical chillers. |
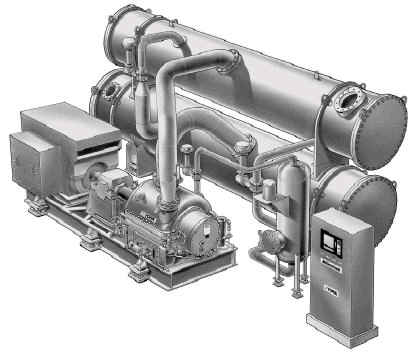 |
| Engine-driven chillers employ an engine to replace the
electric motor of a conventional vapor compression chiller. They
have the potential to reduce your electric energy charges,
because you provide the
energy needed by the chiller, not the electric company. You are
able to avoid the high electricity prices during peak demand
periods, and
maximize savings in areas with extended ratchet electricity rates. |
| |
| Engine-driven chillers are an
excellent source of high-temperature waste heat, which can be
used for water heating, process heating, or steam production. |
|
| |
Summary of
Advantages |
| |
- Used where hot water/steam is
needed
- Higher part-load efficiency
- Variable-speed operation
- Produces high-temperature Waste Heat
- Reduce Peak Electricity Demand
Charges
|
|
| |
Get More Information |
| |
|
| |
Cost/Benefit
Estimator Tool |
| |
The
Cost/Benefit Tool
allows you to
estimate the potential savings over a typical electric chiller. The
Tool also provides estimates of monthly payments, determine fuel
usage, and simple payback
time. |
| |
|